Uncertainty can lead to:
- non-conforming entities being incorrectly passed on inspection – customer risk, α
- correctly conforming entities being incorrectly failed on inspection – supplier risk, β
particularly when a test result is close to a specification limit.
As exemplified in Figure (a), a test result, apparently within limits, might actually be non-conforming since the ‘tail’ of the probability distribution function extends slightly beyond the limit.

Example: Customer risk (by variable)
Example: Supplier risk (by variable)
– for test result, ym, (distribution gtest)
Example: Customer attribute risk 
_______________________________
Uncertainty can also lead to ambiguity when assessing the significance in general of an apparent difference in pairs of measurement results, for instance as obtained from two different measurement methods. As shown in Figure(b), two measurement results can be examined as to whether they are significantly different by assessing the distance in entity value separating the two distributions PDF.
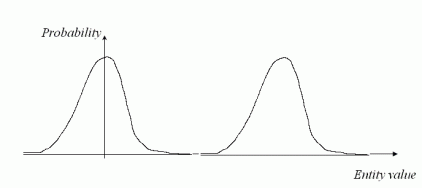
There is, as is well known, a complete set of statistical significance tests for distributions of individual and average values, as well as tests of variances. These include for variables the t-test and Normal tests to determine whether an unknown population mean differs from a standard population mean, and the χ2-test and F-test to determine whether an unknown population standard deviation is greater or less than a standard value [Ferris et al 1946, Montgomery 1996]. Corresponding tests when sampling by attribute can be based on the binomial and Poisson distributions [Joglekar 2003]. The comparison and significance testing of multiple populations can be tackled by conducting analysis of variance (ANOVA) [Joglekar 2003].
Risks and the consequences of incorrect decision-making in conformity assessment should be evaluated. They can be minimised by setting limits on maximum permissible measurement uncertainties and on maximum permissible consequence costs.




